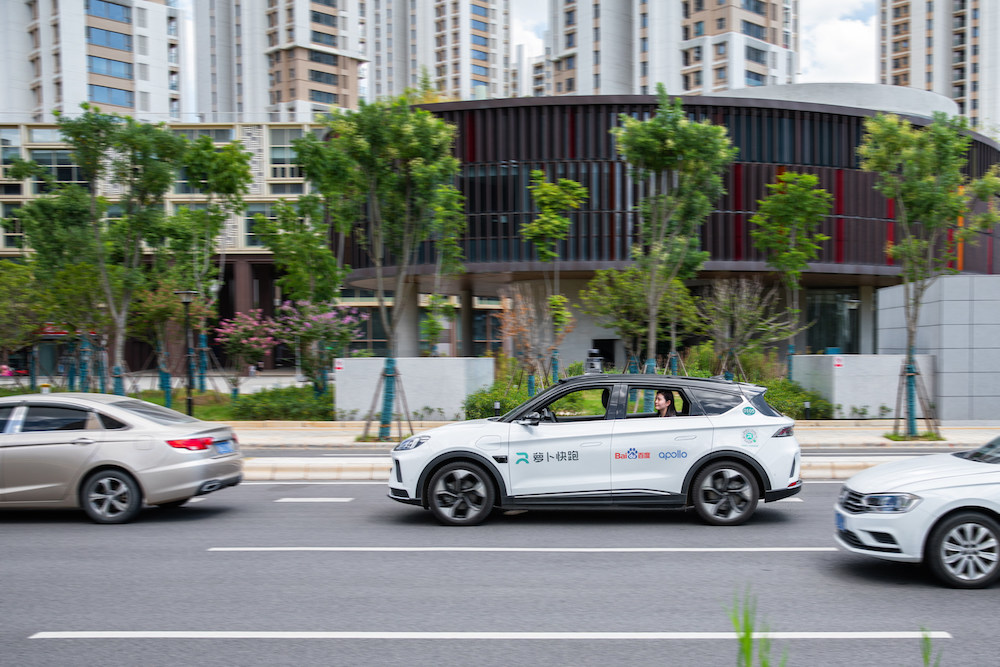
Chinese search giant Baidu has become the first and so far only company in China to secure a permit to offer fully driverless robotaxi services on open roads to the public, without human drivers in the car, the company announced August 8.
Apollo Go, Baidu’s autonomous ride-hailing service, is now authorized to collect fares for robotaxi rides in Chongqing and Wuhan, two of China’s largest megacities.
“This is a tremendous qualitative change,” Wei Dong, vice president and chief safety operation officer of Baidu’s intelligent driving group, said in a statement. “Fully driverless cars providing rides on open roads to paying customers means we have finally come to the moment that the industry has been longing for. We believe these permits are a key milestone on the path to the inflection point when the industry can finally roll out fully autonomous driving services at scale.”
Both Wuhan and Chongqing have been pioneering new approaches to intelligent transportation in recent years. For instance, the Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone has revamped 321 kilometers of roads for testing of autonomous vehicles since 2021, of which 106 kilometers are covered by a 5G-powered vehicle-to-everything communications system. Chongqing has designated an area in its Yongchuan district as a pilot zone for autonomous driving, in which 30 robotaxis have accumulated a test mileage of 1 million kilometers.
Baidu will now begin to provide fully driverless robotaxi services on specially designated open roads in Wuhan from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. and Chongqing from 9:30 a.m. to 4:30 p.m., with five Apollo fifth-generation robotaxis operating in each city. The areas of service cover 13 square kilometers in the Wuhan Economic & Technological Development Zone and 30 square kilometers in Chongqing’s Yongchuan district.
To receive the permits, Baidu’s robotaxis underwent multiple steps of testing and licensing, starting from testing with a safety operator in the driving seat, to testing with a safety operator in the passenger seat, before finally receiving authorization to operate with no human driver or operator in the vehicle.
As the only company granted such permits from two Chinese megacities, Baidu’s robotaxis come with multiple mechanisms to ensure ultimate safety, including an autonomous driving system, monitoring redundancy, remote driving capability and a robust safety operation system, all of which are backed by a massive trove of real-world data, including a total test mileage of over 32 million kilometers driven by Baidu’s autonomous vehicles to date.