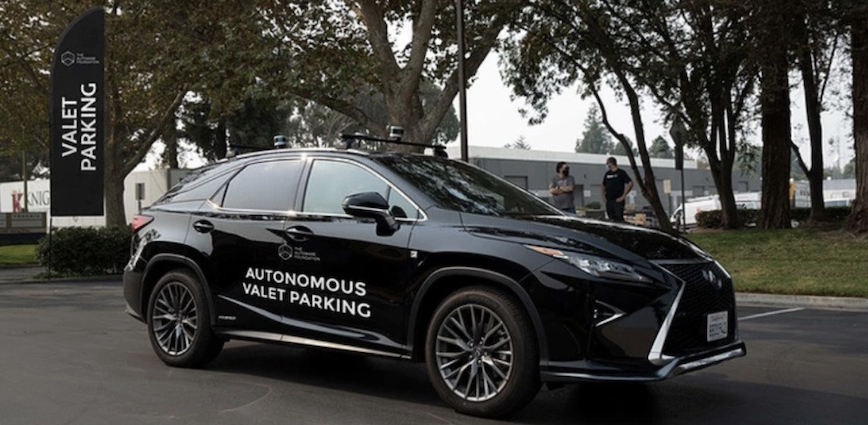
The Autoware Foundation (AWF) has released a new module of its open-source software that supports the autonomous valet parking (AVP) operational design domain (ODD). The AWF team validated a range of core autonomous driving (AD) algorithms and scenarios which will be the basis for support of more complex ODDs in future releases of Autoware.Auto.

Autoware is an open-source operating system for autonomous vehicles containing all the major components necessary: localization, mapping, route planning, vehicle/pedestrian identification, tracking, simulation, lane detection, sensor drivers/fusion and more.
The features and capabilities in Autoware.Auto V1.0.0 release enable autonomous vehicles to perform autonomous parking based on dynamic planning with HD maps; autonomous parking using waypoint following without HD maps; and either of the above with and without obstacle detection, avoidance, and stopping. The release also enables integration of the vehicle’s AD system with a web services platform over a wireless network to initiate and manage AVP functionality.
Josh Whitley, senior software architect for the Autoware Foundation, coordinated the project, with software contributions from Arm, Apex.ai, Embotech, Mapless.ai, Open Robotics, Parkopedia, Robotec AI, and Tier IV.
Autoware.Auto ODD Roadmap
The Autoware.Auto Open Source Software (OSS) project will continue to evolve based on the concept of incrementally adding features and functionality targeting well defined ODDs, with the ultimate goal of achieving L4/L5 autonomous driving in any operational environment (e.g. robo-taxis operating in dense urban environments). By targeting incrementally more complex ODDs (e.g. higher speeds, traffic density, pedestrians, weather conditions, etc.), the developer community contributing to the advancement of the Autoware.Auto project will be presented with a manageable set of development and verification tasks to address the requirements for the future releases of Autoware.Auto.
Based on this approach, the next ODDs that the Autoware.Auto project will address have been decided to be the Cargo Delivery and Racing ODDs. Cargo Delivery represents a broad range of applications and use cases for autonomous vehicles, typically at lower speeds and in more constrained environments.
Racing has always played an important role in the advancement of automotive technology, and this trend is expected to continue in the area of autonomous driving technology. Safe maneuvering (passing) at high speeds (up to 300kph) in a well constrained environment (race track) will advance the Autoware.Auto AD software stack localization, perception, planning and control functionality.
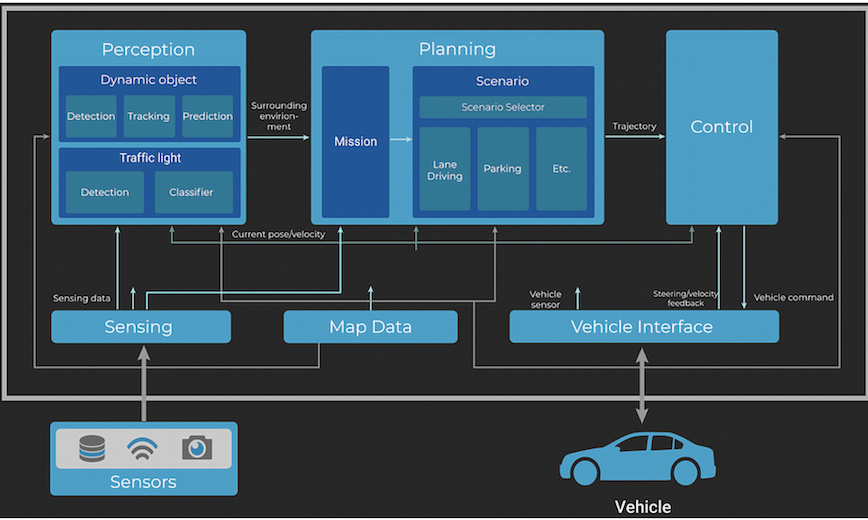
Autoware.Auto architecture for L4/L5 AD
Beyond the currently selected ODDs, the Autoware Foundation is evaluating the options for future ODDs on the path to achieving L4/L5 AD in complex operational environments based on technical complexity, business opportunities, ecosystem and alliance development.
In addition to the continued advancement of Autoware.Auto, the Autoware Foundation will continue to engage with foundation members and the broader AD ecosystem to integrate their products and solutions into the reference implementations, tools and services which are utilized for development and validation of AD systems based on Autoware. These topics are addressed under the Autoware.IO project.
The non-profit Autoware Foundation has more than 50 members, including Hexagon | AutonomouStuff as a core participant. The U.S. Department of Transportation’s Federal Highway Administration recently joined also, fleshing out the line-up of autonomy integrators, sensor companies, semiconductor companies, and other research institutions.