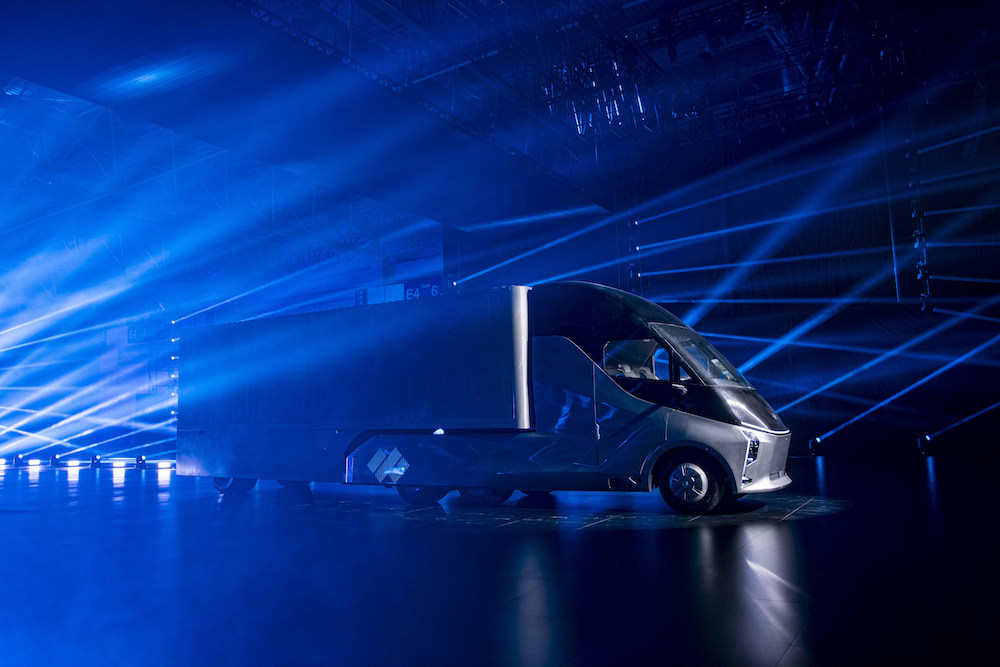
Chinese search giant Baidu’s subsidiary DeepWay has unveiled a new robot truck with which it aims to automate road freight, the company announced Sept. 17.
The new heavy-duty truck, named Xingtu, is armed with a computing power of more than 500 trillion operations per second. Equipped with 10 onboard cameras, 5 millimeter-wave radars and 3 infrared detectors, Xingtu can achieve end-to-end autonomous driving—from perception to planning—within 100 milliseconds, and ultra-long-range sensing capabilities of more than 1 kilometer.
“This new generation of vehicle is by no means just a modified truck—it’s a robot truck,” Yunpeng Wang, vice president and general manager of autonomous driving technology at Baidu, said in a statement.
The Apollo autonomous driving platform technology underlying DeepWay’s Xingtu has been developed by Baidu since 2013 and has nearly 8.7 million test miles. The Baidu Apollo Go robotaxi service powered by this system, now operational in Beijing and two other cities in China, has carried more than 210,000 passengers.
DeepWay is a joint venture company created by Baidu and Waltham, Massachusetts-based Lionbridge Technologies in 2020 to focus on the development and manufacturing of smart new heavy-duty trucks. Xingtu marks Baidu’s entry into the multi-trillion-dollar global freight market.
The company noted Xingtu’s lightweight integrated battery and chassis design greatly reduces wind resistance and improves energy efficiency. In simulation tests with the China Automobile Research Institute, the new truck showed a wind resistance coefficient as low at 0.35, reducing overall energy consumption.
At a full load of 49 tons, Xingtu’s custom-developed 450-kilowatt-hour battery pack can travel up to 300 kilometers on a single charge, and charges in just one hour at one ampere per second. In addition, DeepWay has also developed a quick-swap solution for the battery, which enables freight drivers to swap out their battery in six minutes. All of this together can reduce energy, maintenance and operation costs, as well as transportation time.
Xingtu also possesses what Baidu called a smart cabin, which adopts the concept of separate driving, working and living spaces, giving more room to the drivers. Equipped with an intelligent voice assistant, a large touch screen infotainment system and ultra-comfortable seats and beds, the company noted that freight drivers will experience a much more comfortable working and living environment while on the road.
The first generation of Xingtu is designed to enable Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) Level 3 autonomy on high-speed freight routes—that is, the automated driving system can drive the vehicle instead of the driver in some circumstances, but requires a human driver to take control if the system demands. Baidu’s plan is to achieve SAE level 4 capabilities on these same routes between 2024 and 2026—that is, able to act without any human intervention in the vast majority of situations.