At the ADAS & Autonomous Vehicle Technology Expo and Conference in San Jose, CA this week, dSPACE GmbH showed its Simphera software solution for simulating and validating autonomous driving applications.
The solution received certification from TÜV Süd — the international, independent specialist in testing, inspection, and certification — for ISO 26262 for safety-related systems just nine months after its launch. Automotive manufacturers and suppliers can now exempt Simphera from the qualification of their overall processes according to ISO 26262, instead focusing on proving the functional safety of their own highly complex process chains.
dSPACE is a leading provider of simulation and validation solutions for developing vehicles, focusing most recently on connected, autonomous, and electric vehicles. The company’s range of end-to-end solutions is used particularly by automotive manufacturers and their suppliers to test the software and hardware components in their new vehicles before they hit the road. With more than 2000 employees worldwide, the Paderborn, Germany-headquartered supplier has three project centers in Germany and serves customers through regional companies in the U.S., the UK, France, Japan, China, Croatia, and South Korea.
Following the successful initial ISO 26262 certification, dSPACE and TÜV Süd plan to jointly develop a new procedure for the continuous certification of software products, such as Simphera, developed in an agile manner according to the functional safety standard. This will enable for the validation of new features and functions for autonomous driving more quickly and safely.
“We want our customers to be able to focus on their core competencies when developing applications for autonomous driving functions, and to use dSPACE’s tools with the certainty that the functions developed with them will meet the highest industry standards in terms of functional safety,” said Tino Schulze, Executive Vice President for Automated Driving & Software Solutions at dSPACE.
The web-based, highly scalable cloud solution lets users perform the computation-intensive validation of functions for autonomous driving quickly and easily, supports the collaboration of development teams that are distributed worldwide, and lets customers easily integrate their applications. Reusable models, scenarios, tests, and interfaces allow for continuous testing on software- and hardware-in-the-loop (SIL and HIL) platforms.
According to dSPACE, the development of functions for greater vehicle autonomy places increasingly strict requirements on the quality and safety of functions, resulting in a skyrocketing number of tests that need a large and scalable computing infrastructure. In addition, virtual tests are front-loaded to earlier phases of development, where they are executed by development teams distributed around the world.
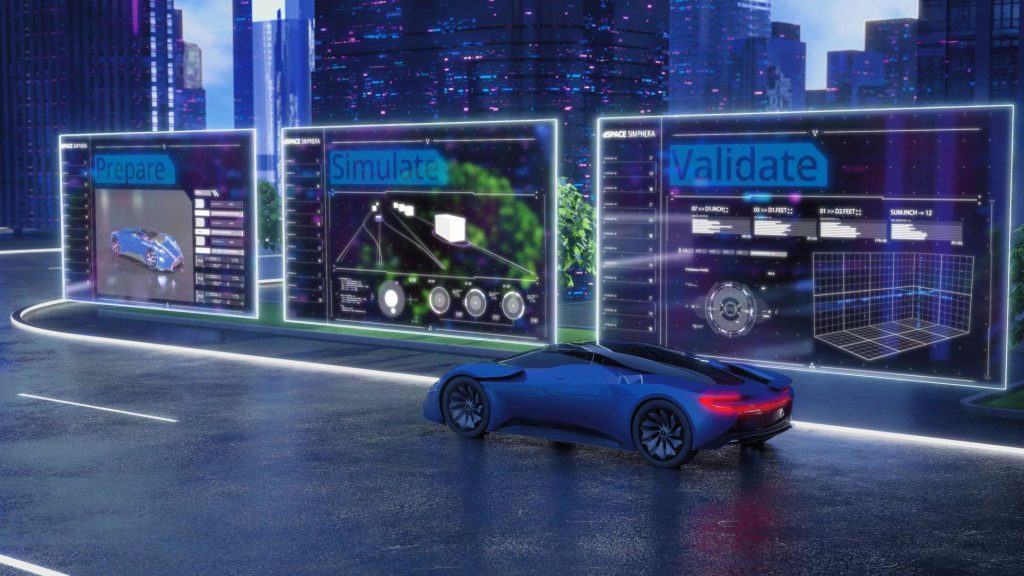
The company had this in mind when it developed the new web-based solution that provides three components.
The Prepare component gives users tools to generate and modify the artifacts required for specific development or validation tasks. This can include proprietary simulation models such as vehicle, sensor, roads, traffic, and environment models or scenarios.
For the Simulate component, the prepared models and scenarios are used for interactive simulations. Users can check the desired algorithm behavior with a range of visualization and measurement functions.
The functions of the Validate component help users perform scenario-based testing on a large scale. Intelligent variations of parameters in a scenario can turn a handful of logical scenarios into a number of specific test cases that can be rapidly processed and analyzed in more detail.
The initial Simphera release is focused on validation solutions for functions related to autonomous driving, scenario-based testing, and SIL testing. The reusable models, scenarios, tests, and interfaces allow for an easy transition to automated tests on HIL platforms. The solution supports traceability in troubleshooting, lowers costs, and accelerates development and homologation.
“Simphera will make life easier for developers in all phases of development and validation—from the initial idea of an algorithm to the release test of an ECU,” said Schulze at the solution’s launch. “By providing this integrated solution, we not only accelerate development but also make it more efficient, thereby, increasing our customers’ return on investment.”
Simphera is one of the latest and most significant autonomy-related announcements from the supplier.
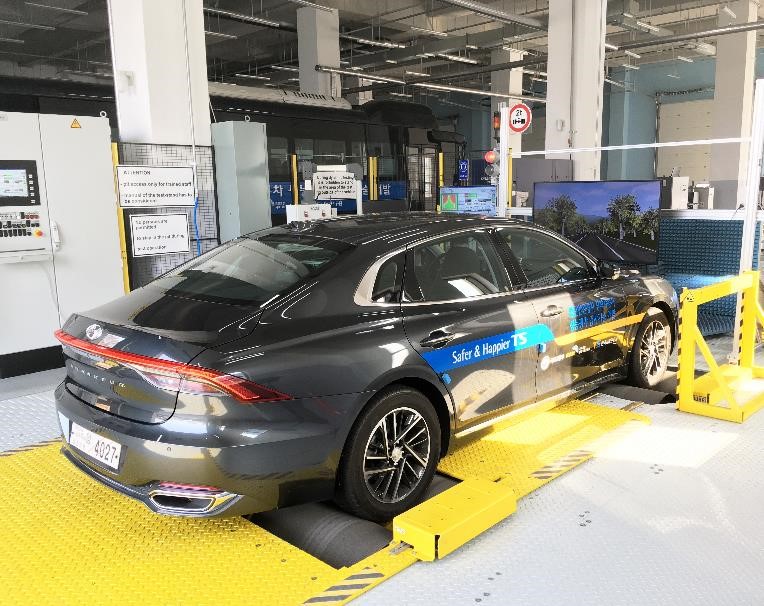

In June, dSPACE announced its cooperation with Dürr Assembly Products in the launch of an x-road curve multi-function test stand for autonomous and partially autonomous vehicles in Korea for the Korea Transportation Safety Authority, a public authority responsible for vehicle and traffic safety. Unlike with conventional roll test stands, the x-road curve permits free driving with steering movements to simulate cornering. In combination with the virtual environments developed by dSPACE, typical traffic situations are simulated to elicit a response from the sensors installed in the vehicle, enabling the functionality of driver assistance systems to be tested.
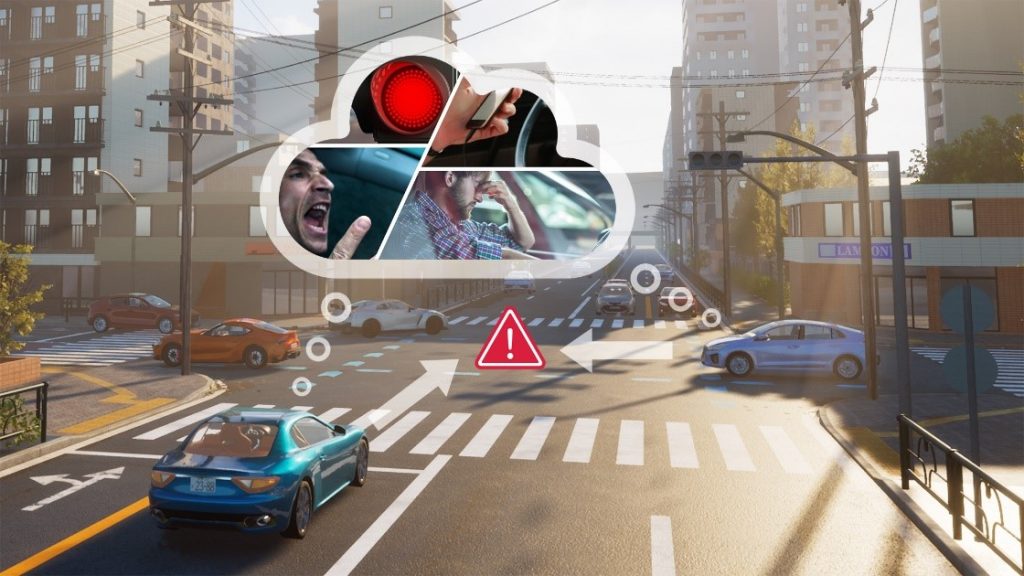

In April, dSPACE announced it was working with CogniBIT to make traffic scenarios for the development and testing of autonomous vehicles more realistic. In the first stage, dSPACE is pairing its simulation environment Automotive Simulation Models (ASM) with DriveBOT, CogniBIT’s AI-based driver model, to integrate unpredictable behavior of human drivers into the simulation. In the future, behavior models from further road users, such as pedestrians or motorcyclists, will be integrated into simulations.
Traffic situations are influenced by the behavior of individual road users, which includes emotions such as fear, surprise, and happiness but also limitations such as the road users’ impaired view. The partners believe that highly automated and autonomous driving will become safer in practice only when all of these aspects are realistically integrated into the simulation for the development and testing of functions. DriveBOT lets users replicate human-like behavior in the simulation and reproduce realistic traffic scenarios.