Baidu has unveiled its next-generation autonomous vehicle (AV) called Apollo RT6, an all-electric, production-ready model designed for complex urban environments. With a cost of just RMB 250,000 (about $37,000), the company hopes the SAE Level 4 AV’s arrival will accelerate automated driving deployment at scale, bringing the world closer to a future of driverless shared mobility.
The RT6’s creation marks another milestone for Baidu in achieving its goal of providing safer, greener, and more efficient mobility solutions. The AV will be put into operation in China in 2023 on the company’s Apollo Go autonomous ride-hailing service. Described by Baidu as the world’s largest robotaxi service provider, Apollo Go has expanded to 10 cities in China since its launch in 2020, including all first-tier cities, and provided more than 1 million service orders.
“This massive cost reduction will enable us to deploy tens of thousands of AVs across China,” said Robin Li, Co-founder and CEO of Baidu, at Baidu World 2022, the company’s flagship technology conference, in Beijing. “We are moving towards a future where taking a robotaxi will be half the cost of taking a taxi today.”
Featuring Baidu’s sixth generation of AV tech, the Apollo RT6 is distinct from previous generations in being a clean-sheet design and not retrofitted from conventional vehicles. Its design consolidates features of SUVs and MPVs.

Robin Li, Co-founder and CEO of Baidu, speaking at Baidu World 2022.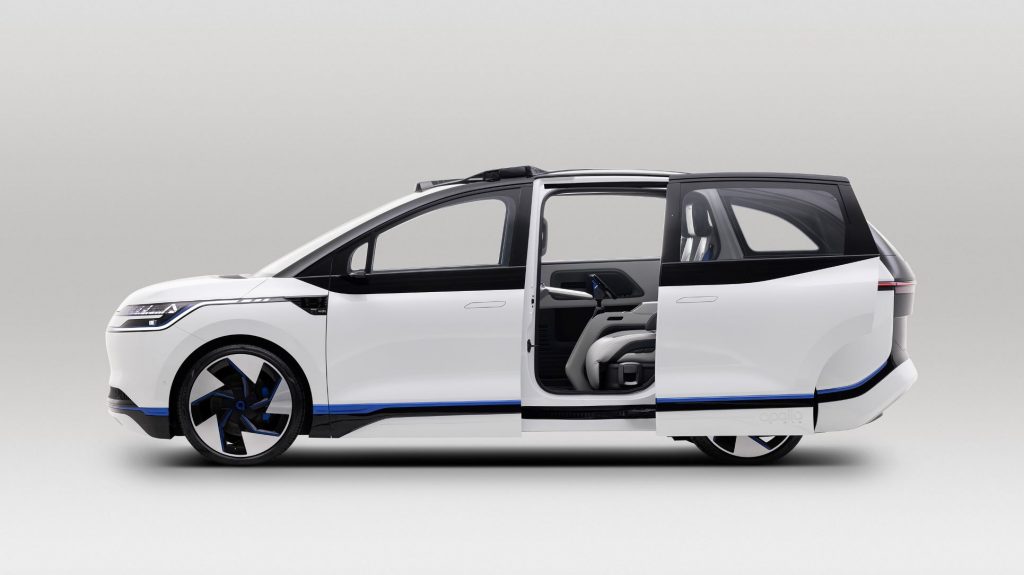 
Baidu Apollo RT6 has sliding doors for easy access.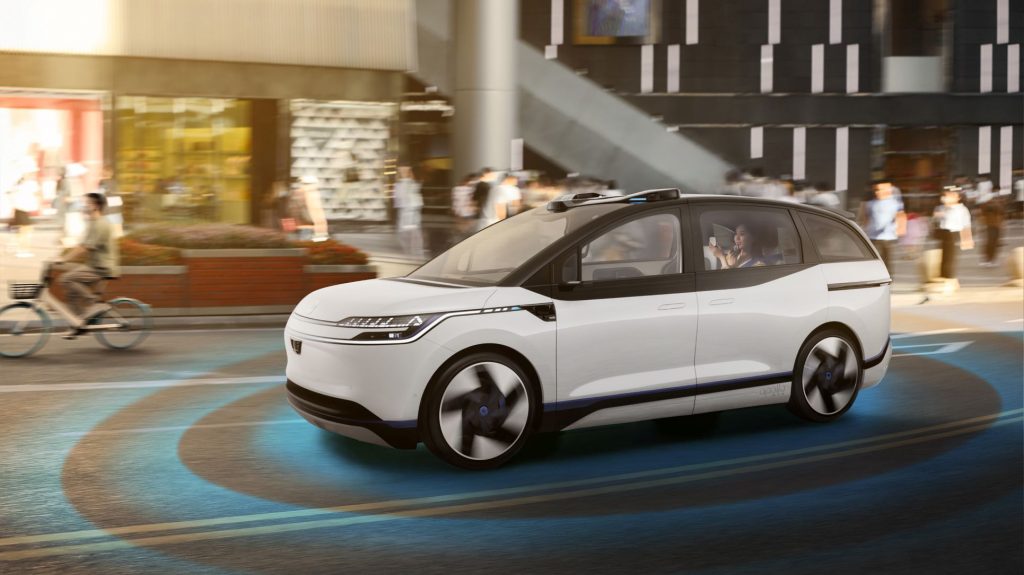 
Baidu Apollo RT6 will deploy on the Apollo Go network.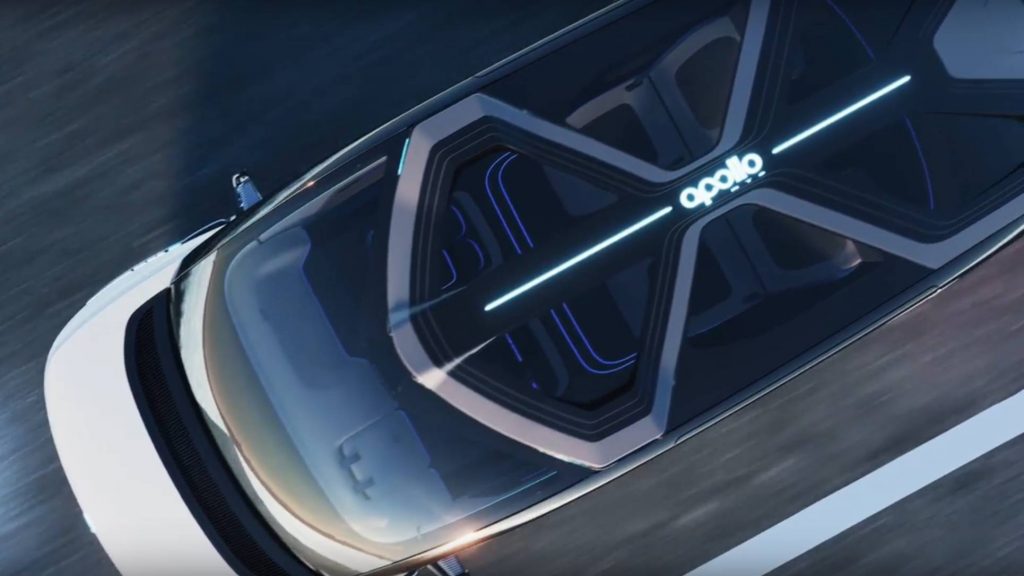 
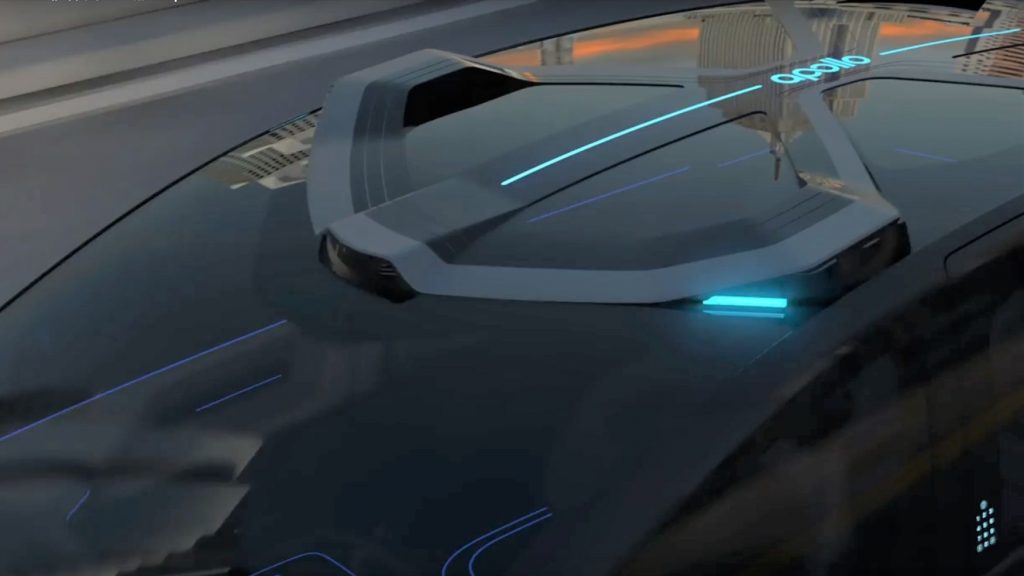

Baidu Apollo RT6 rooftop sensor array closeup.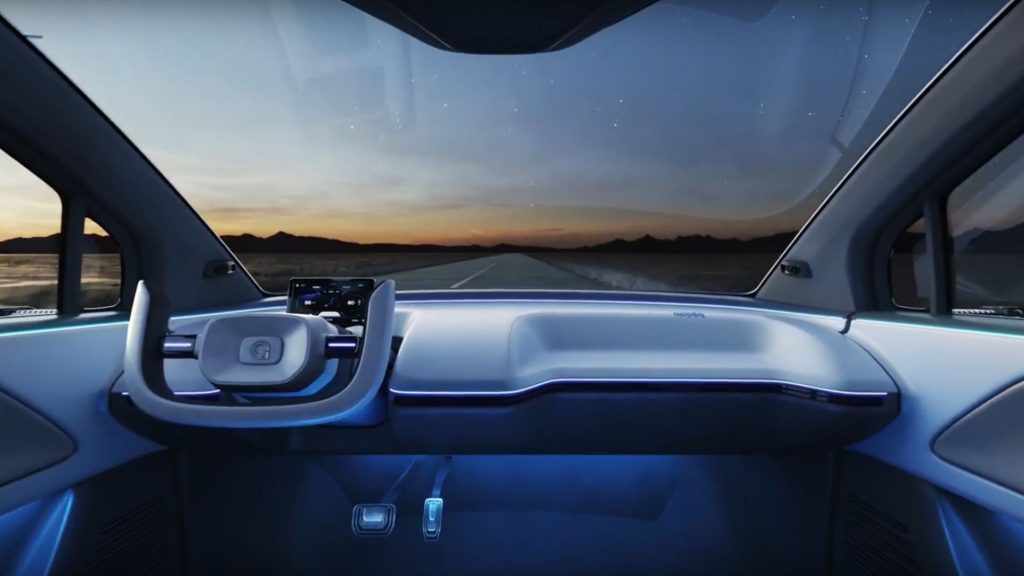 
Baidu Apollo RT6 interior with deployed steering wheel.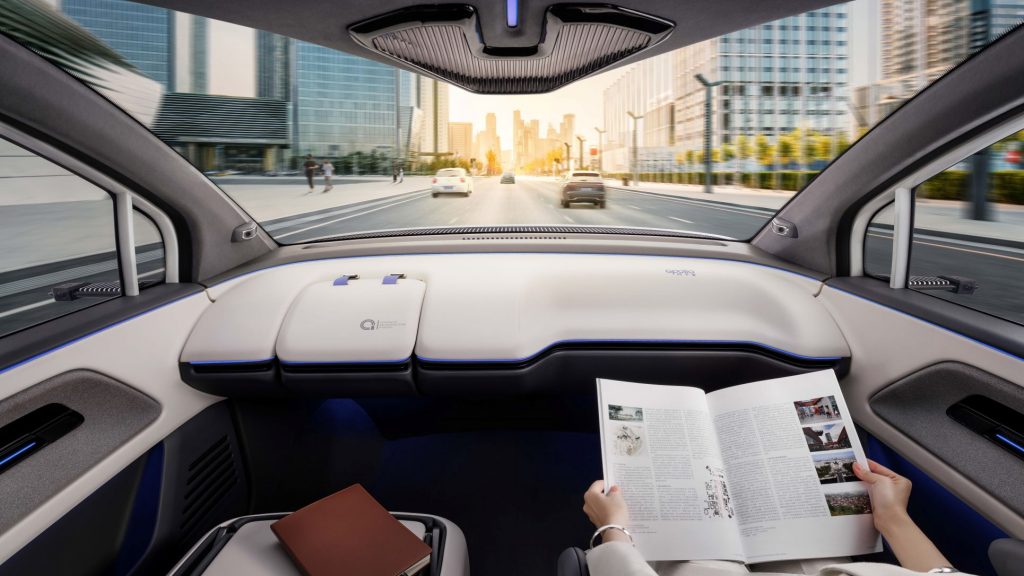 
Baidu Apollo RT6 interior without deployed steering wheel.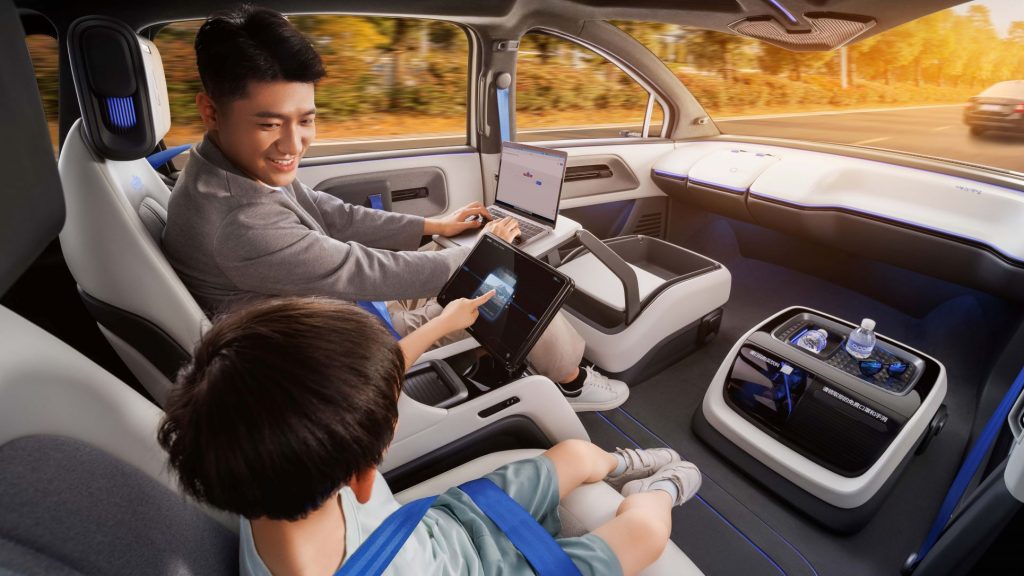 
The retractable steering wheel unlocks gives Apollo RT6 more versatile in-car experience.
The RT6’s exterior features intelligent electric sliding doors to ease passenger entry and exit. Its roof integrates sensors and an intelligent interaction system featuring lights to communicate with passengers and other cars on the road. Mechanically, its safety package adds a “super high-strength cage” body design and rear-facing enhanced safety protection for a promised five-star safety anti-collision rating.
Inside, a stowable steering wheel can give more space for unique interior configurations, allowing for the installation of extra seating, vending machines, desktops, and/or gaming consoles. At 4760 mm (187.4 in) long, 1870 mm (73.6 in) wide, and 1650 mm (65.0 in) tall, with a wheelbase of 2830 mm (114.4 in), Baidu is aiming for a “rider-first” AV with a flat floor that delivers comfort with independent rear seating and ample 1050-mm (41.3 in) rear legroom. The company claims A-class size in wheelbase, but B-class rear seat legroom and a C-class experience.
The AV integrates Baidu’s most advanced L4 autonomous driving system powered by automotive-grade dual-computing units with up to 1200 TOPS (tera operations per second). The vehicle uses 38 sensors—8 LiDARs, 6 millimeter-wave radars, 12 ultrasonics, and 12 cameras—for long-range detection on all sides. Its safety and reliability are backed by massive amounts of real-world data for a total of over 32 million km (20 million mi) driven by Baidu’s AVs to date.
At Baidu World, Zhenyu Li, Senior Corporate Vice President of Baidu and General Manager of its IDG (Intelligent Driving Group), said the autonomous driving capability of the Apollo RT6 is equivalent to a skilled driver with 20 years of experience.
It will be the first vehicle model built on Xinghe, Baidu’s proprietary automotive E/E (electrical/electronic) architecture specially developed for fully autonomous driving. The vehicle is said to be 100% automotive-grade and has full redundancy throughout both hardware and autonomous driving software. It is said to feature the industry’s first seven-layered full redundancy system—for power, communication, L4 braking, L4 steering, architecture, computing unit, and sensor.
The RT6’s Apollo OS features the industry’s highest safety level, receiving the Baidu says is the industry’s first ISO 26262 ASIL-D certification for functional safety of autonomous driving. Its integrated fault diagnosis and risk downgrading system is supported by hardware and the autonomous driving system.
Regarding the mass production and deployment timeline, Baidu plans to have a large fleet of mass-produced RT6 put into trial operation on Apollo Go targeting the second half of 2023. In April, the company received the first-ever permits in China authorizing it to provide driverless ride-hailing services to the public on open roads in Beijing.
The size of the RT6 fleet is planned to be expanded at a consistent pace from 10,000 to 100,000 units. Apollo Go plans to expand its ride-hailing service to 65 cities by 2025 and 100 cities in 2030.