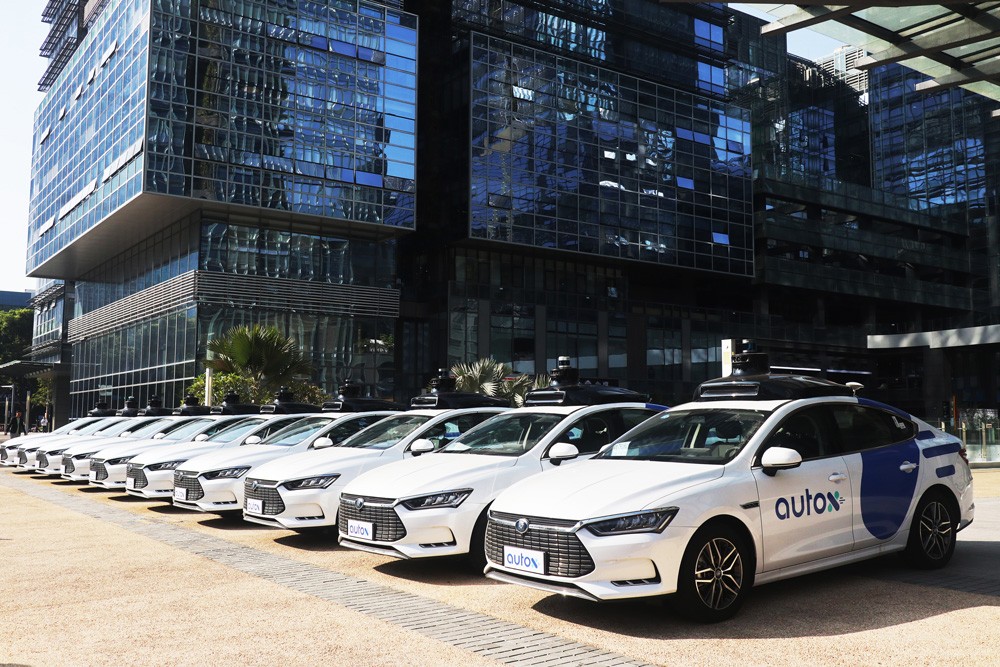
Self-driving cars now rove the streets in Shenzhen, China, fielded in beta testing by AutoX, an Alibaba-backed Chinese autonomous car technology firm. The fleet of 25 is completely autonomous, with no accompanying human drivers or remote operators, as has been the case in other robotaxi tests across China; those vehicles still have a driver who can take over in emergencies or who can operate the car remotely.

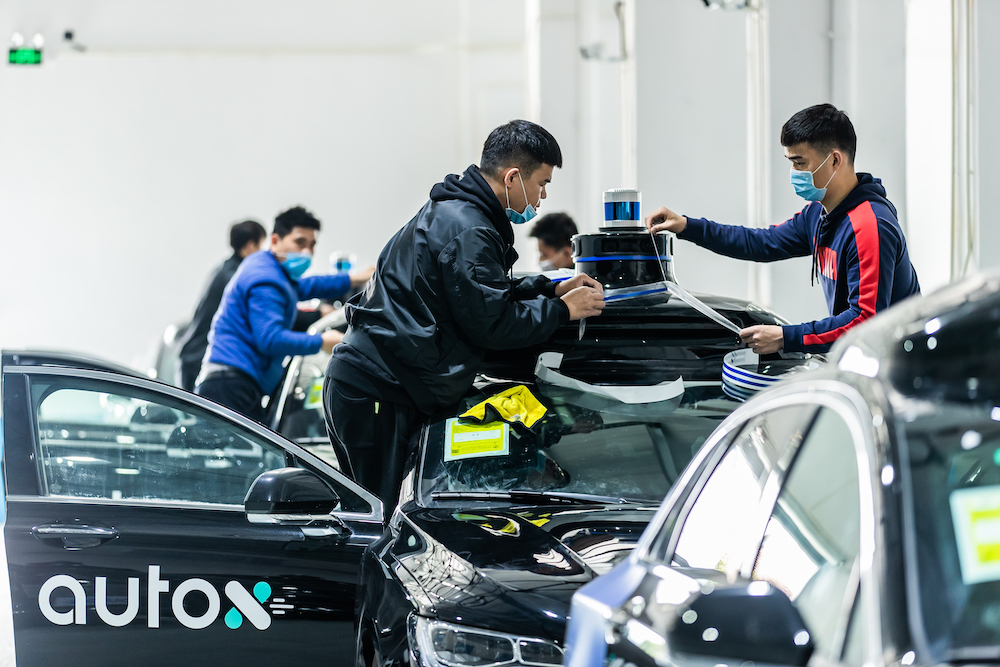
The AutoX Shenzhen fleet is not yet available to the general public. Company employees and private guests, media, business partners, investors and auto-makers comprise the customer testing base.
Next Up: increase the number of cars and the test area size, and test in more cities, said company COO Jewel Li. “We have a plan in the next six months to expand to 10 cities globally. We’re very excited about the Southeast Asia market, we think this is the next rising market.”
“It’s close to a sci-fi kind of experience for most of our riders. When you really experience the vehicle fully driving itself, the level of excitement is overwhelming.” she added.
AutoX also has a pilot self-driving taxi service in Shanghai and a permit to test driverless cars without a safety driver in parts of San Jose, California.

Meanwhile in Beijing. Search-engine firm Baidu Inc will conduct road tests for five fully driverless vehicles in China’s capital. These tests will gradually reduce human intervention and eventually remove in-car safety drivers from the autonomous vehicle tests.
According to Beijing safety requirements for driverless testing permits, vehicles must have completed more than 30,000 kilometers of safe test driving on open roads and passed an evaluation on a closed track.
Baidu opened Apollo Go Robotaxi to the public in Beijing in October. Each of the driverless taxis has a backup driver, who is ready to take manual control in an emergency.
China plans to start scale production of vehicles capable of conditional autonomous driving and commercialization of highly autonomous vehicles in defined conditions by 2025.